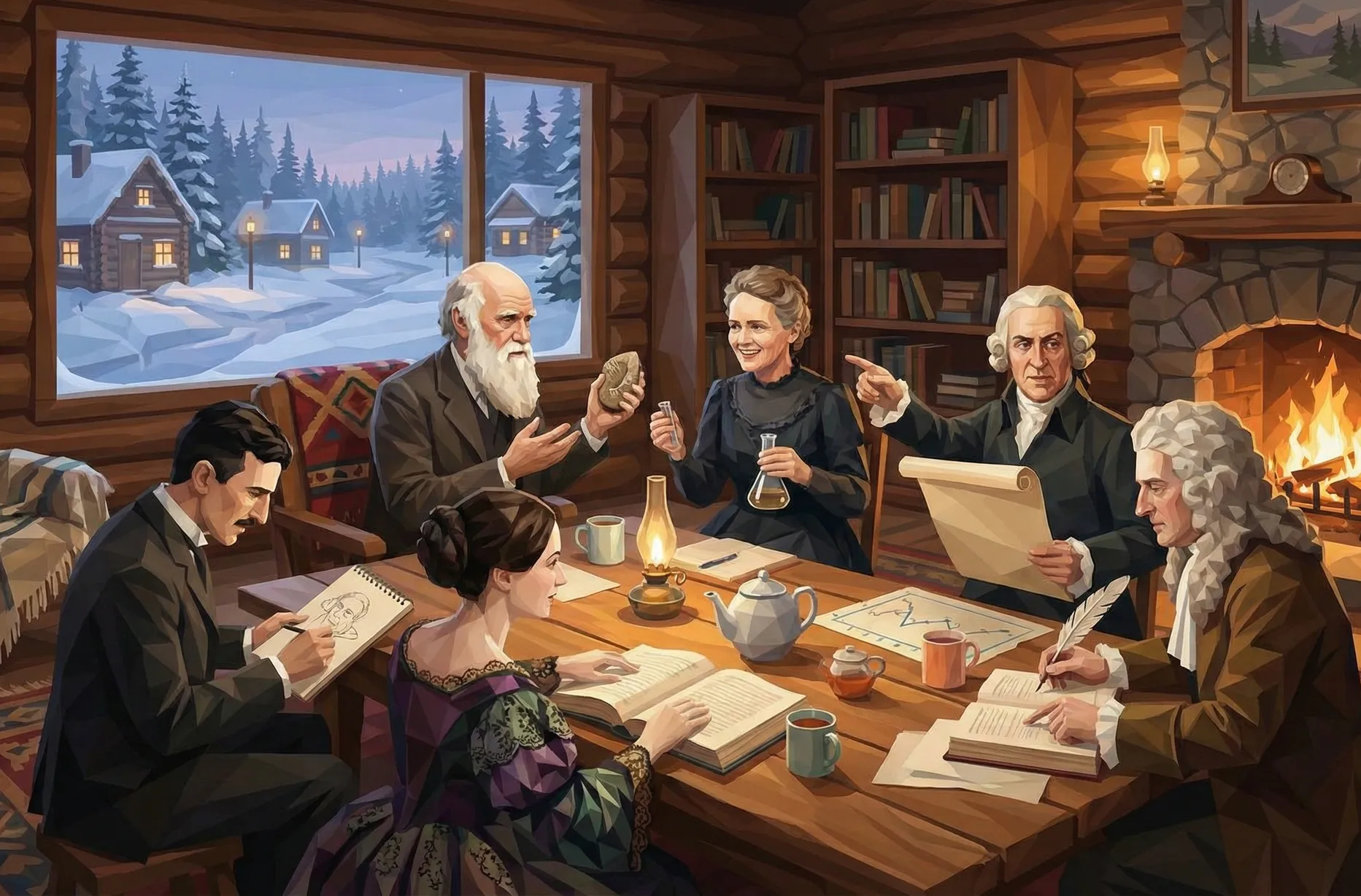
1. Choose Your Module
platform.grassroot.academy
Explore Courses
Search courses...
All
Mathematics
Science
CS
Economics
AP Calculus AB
Rice University
High School
Math
AP Chemistry
Rice University
High School
Chemistry

AP Biology
Rice University
High School
Biology
Agentic AI
Grassroot Original
Professional
Tech

Algebra 1
BCcampus OpenEd
High School
Math
AP Computer Science A
Rice University
High School
CS

Intro to Investing
Grassroot Original
Professional
Finance

AP Macroeconomics
Rice University
High School
Econ
Geometry
BCcampus OpenEd
High School
Math
High School Physics
BCcampus OpenEd
High School
Physics

SAT Reading & Writing
College Board
High School
English

Intro to Vibe Coding
Grassroot Original
Professional
Tech

Algorithmic Trading
Grassroot Original
Professional
Finance

AP Statistics
Rice University
High School
Math

AP Physics 1
Rice University
High School
Physics

Intro to Data Science
BCcampus OpenEd
College
CS

SAT Math
College Board
High School
Math

Startups 101
Grassroot Original
Professional
Business

AP Calculus AB
Rice University
High School
Math

AP Chemistry
Rice University
High School
Chemistry

AP Biology
Rice University
High School
Biology

Agentic AI
Grassroot Original
Professional
Tech

Algebra 1
BCcampus OpenEd
High School
Math
AP Computer Science A
Rice University
High School
CS

Intro to Investing
Grassroot Original
Professional
Finance

AP Macroeconomics
Rice University
High School
Econ

Geometry
BCcampus OpenEd
High School
Math
High School Physics
BCcampus OpenEd
High School
Physics

SAT Reading & Writing
College Board
High School
English

Intro to Vibe Coding
Grassroot Original
Professional
Tech

Algorithmic Trading
Grassroot Original
Professional
Finance

AP Statistics
Rice University
High School
Math

AP Physics 1
Rice University
High School
Physics

Intro to Data Science
BCcampus OpenEd
College
CS

SAT Math
College Board
High School
Math

Startups 101
Grassroot Original
Professional
Business
From our library of official and community-generated modules
platform.grassroot.academy
Create a new module
×
Module name *
Organic Chemistry 1
Choose Your Tutor
Add materials (optional)
Upload a file
PDF, Word, or text files
Cancel
Create module
Create a new module
×
Module name *
Organic Chemistry 1
Add materials (optional)
lecture-notes.pdf
×
Creating chapters...
✓ Reading
✓ Analyzing
✓ Extracting
Organizing
Cancel
Creating...
Organic Chemistry 1
Practice
Learn
Start Learn
Atomic Structure
Atomic theory, bonding, and electron configuration
4
2
Molecular Geometry
VSEPR, hybridization, and molecular polarity
5
3
Chemical Reactions
Reaction types, equations, and mechanisms
4
4
Stoichiometry
Mole concept, limiting reagents, and yield
3
5
Thermochemistry
Enthalpy, Hess's law, and calorimetry
4
6
Acids & Bases
pH scale, buffers, and titration curves
3
Chapter 1
Atomic Structure & Bonding
Atomic theory, bonding, and electron configuration
Concepts (4)
1
Atomic Theory & Models
Dalton, Thomson, Rutherford, and Bohr models of the atom
2
Electron Configuration
Orbital filling, quantum numbers, and periodic trends
3
Chemical Bonds
Ionic, covalent, and metallic bonding types
4
Lewis Structures
Drawing dot structures and predicting molecular shape
Chapter 2
Molecular Geometry & Polarity
VSEPR, hybridization, and molecular polarity
Concepts (5)
1
VSEPR Theory
Predicting molecular shapes from electron pair repulsion
2
Hybridization
sp, sp2, sp3 orbital mixing and bond angles
3
Molecular Polarity
Dipole moments and electronegativity differences
4
Intermolecular Forces
Van der Waals, hydrogen bonding, dipole interactions
5
3D Molecular Shape
Visualizing tetrahedral, trigonal, and linear geometry
Chapter 3
Chemical Reactions & Equations
Reaction types, equations, and mechanisms
Concepts (4)
1
Types of Reactions
Synthesis, decomposition, combustion, and redox reactions
2
Balancing Equations
Conservation of mass and systematic balancing methods
3
Reaction Mechanisms
Elementary steps, intermediates, and rate-determining step
4
Catalysis
Homogeneous and heterogeneous catalytic pathways
Chapter 4
Stoichiometry & Calculations
Mole concept, limiting reagents, and yield
Concepts (3)
1
Mole Concept
Avogadro's number, molar mass, and conversions
2
Limiting Reagents
Identifying limiting reactants and excess amounts
3
Percent Yield
Theoretical, actual, and percent yield calculations
Chapter 5
Thermochemistry & Energy
Enthalpy, Hess's law, and calorimetry
Concepts (4)
1
Enthalpy Changes
Exothermic and endothermic reaction energetics
2
Hess's Law
Calculating enthalpy from reaction pathway summation
3
Calorimetry
Measuring heat transfer in chemical processes
4
Bond Energies
Estimating reaction enthalpy from bond dissociation data
Chapter 6
Acids, Bases & Equilibria
pH scale, buffers, and titration curves
Concepts (3)
1
pH Scale
Hydrogen ion concentration and logarithmic measurements
2
Buffer Solutions
Weak acid/base pairs and resistance to pH change
3
Titration Curves
Equivalence points, indicators, and acid-base pairings
Open
Favorites
Desktop
Documents
Downloads
homework.docx
lecture-notes.pdf
syllabus.pdf
notes-ch3.pdf
lecture-notes.pdf
Cancel
Open
Create your own by uploading materials or using AI research
2. Pick Your Mode
platform.grassroot.academy
ACT English
1)
Production of Writing
0/6
2)
Knowledge of Language
0/4
3)
Standard English
0/14
4)
Key Ideas & Details
0/6
5)
Craft & Structure
0/6
Vocabulary in Context
Author's Purpose
Text Structure
Point of View
Tone & Style
Rhetorical Strategy
Save & Exit
Current
Vocabulary in Context and Word Meaning
Vocabulary in Context means figuring out what a word means by looking at the surrounding sentences—not by memorizing a dictionary definition.
On the ACT, they’re testing whether you can read carefully and use clues from the passage.
The Three Types of Context Clues
1. Definition Clues The passage literally tells you what the word means.
• “The protagonist was sanguine, or optimistic, about her chances.”
2. Contrast Clues The passage shows what the word is NOT.
• “Unlike his gregarious brother, Marcus was withdrawn.”
3. Example Clues The passage gives examples showing what the word means.
• “The coach’s acerbic comments—sarcastic jokes, cutting remarks”
The Golden Rule
Don’t guess in isolation. Plug it into the sentence and ask: “Does this make sense?”
Practice: Vocabulary in Context
Question 1 of 1
•
Timer Off
•
Mastery: 0/2
Concept: Vocabulary in Context
Passage
When I started my first job at a marketing firm, I expected to learn from senior executives. Instead, my most valuable lessons came from the office receptionist, Maria.
One afternoon, she pulled me aside after a difficult client meeting. “You talked too much,” she said bluntly. “The client wanted to explain their problem, but you kept interrupting with solutions.” I felt embarrassed, but I knew she was right.
One afternoon, she pulled me aside after a difficult client meeting. “You talked too much,” she said bluntly. “The client wanted to explain their problem, but you kept interrupting with solutions.” I felt embarrassed, but I knew she was right.
As used in the passage, the word “bluntly” most nearly means:
Frudely and without consideration
Gdirectly and without softening
Hangrily and with hostile intent
Jquietly and with reluctance
Hi! I’m William Shakespeare, your guide through Craft & Structure. You’re at 0/6 mastered—let me set up the key points!
ok
Let’s start with Vocabulary in Context. It’s about using surrounding text to figure out word meanings—way more useful than memorizing a dictionary!
What clues should I look for?
Three types: definition, contrast, and example clues. I’ve added them to your canvas. Ready to try a practice problem?
Continue
Read the passage about Maria. What does “bluntly” most nearly mean in this context?
G
Correct! “Directly and without softening”—Maria was honest, not rude. The context clues show helpful intent.
Ask me anything...
ok
What clues should I look for?
Continue
G
Learn — step-by-step learning to crack difficult assignments
platform.grassroot.academy
SAT Math
1)
Algebra
2)
Advanced Math
Quadratic Functions
Polynomial Operations
Exponential Functions
Rational Expressions
Functions & Notation
3)
Data Analysis
4)
Geometry & Trig
12 concepts selected
MCQ
FRQ
Mixed
Auto-continue
Generate Practice
Save & Exit
Feb 2026
Practice: 5 questions
Question 1 of 5
Hard
Concept: Ratios & Proportions
Alloy A contains 30% gold and Alloy B contains 70% gold. How many grams of Alloy B are needed to combine with Alloy A to produce 200 grams of an alloy that is 55% gold?
A100
B110
C115
D125
Practice: 5 questions
Question 1 of 5
Hard
Concept: Ratios & Proportions
Alloy A contains 30% gold and Alloy B contains 70% gold. How many grams of Alloy B are needed to combine with Alloy A to produce 200 grams of an alloy that is 55% gold?
A100
B110
C115
✓125
Correct!
0.30(200−b) + 0.70b = 110 → 0.4b = 50 → b = 125
Next question →
Explain this Simply
Practice: 5 questions
Question 2 of 5
Medium
Concept: Linear Equations
A budget constraint is modeled by 15x + 25y = 600. If 10 premium items are purchased, how many basic items can be bought?
A20
B22
C23 with remainder
D25
Practice: 5 questions
Question 2 of 5
Medium
Concept: Linear Equations
A budget constraint is modeled by 15x + 25y = 600. If 10 premium items are purchased, how many basic items can be bought?
A20
B22
✓23 with remainder
D25
Correct!
15x + 25(10) = 600 → 15x = 350 → x ≈ 23.3, so 23 with remainder.
Next question →
Explain this Simply
Let's practice Ratios & Proportions! Think about setting up an equation where the total gold equals 55% of 200g.
D
Correct! Let b = grams of Alloy B, so Alloy A = 200−b. Setting up the gold equation: 0.30(200−b) + 0.70b = 0.55(200), which simplifies to 0.4b = 50, giving b = 125.
explain this simply to me
Think of it like mixing paint! You need the final mix to be 55% gold. Alloy A is weak (30%) and B is strong (70%). Since 55% is much closer to B’s strength, you need a lot more B — exactly 125g of B and only 75g of A to get your 200g mix.
A
Not quite. Try substituting y = 10 into the equation 15x + 25y = 600. What value of x satisfies the equation? Think about whether x needs to be a whole number.
D
Not quite either. Let me walk you through it: substituting y = 10 gives 15x + 250 = 600, so 15x = 350 and x = 23.33. Since x isn't a whole number, the answer is C (23 with remainder).
C
That's right! 15x + 250 = 600 gives x ≈ 23.3, which means 23 basic items with a remainder. Great job working through it step by step!
Ask me anything...
D
explain this simply to me
A
D
C
Practice — drill problems and ace the test